Why is security a problem?
- Wireless is a shared medium
- Attackers are relatively anonymous
- End users are poorly educated
- Denial-of-service is very simple
- Automated malicious attacks are increasingly complex
- Tools are freely available
Long distance attack
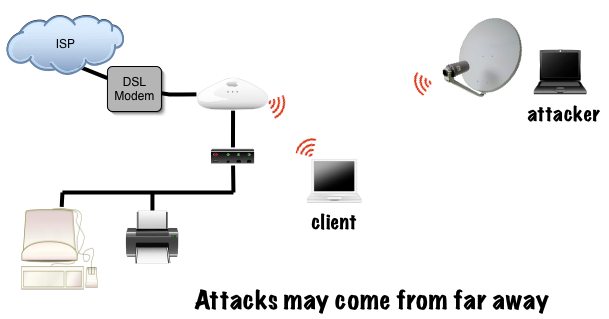
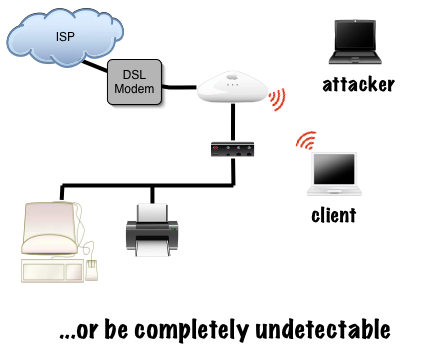
Invisible intruder
Security risks
Who creates security problems?
- Unintentional users
- "War Drivers"
- Rogue access points
- Eavesdroppers (personal and corporate spies)
- Virus-infected computers
- Malicious users
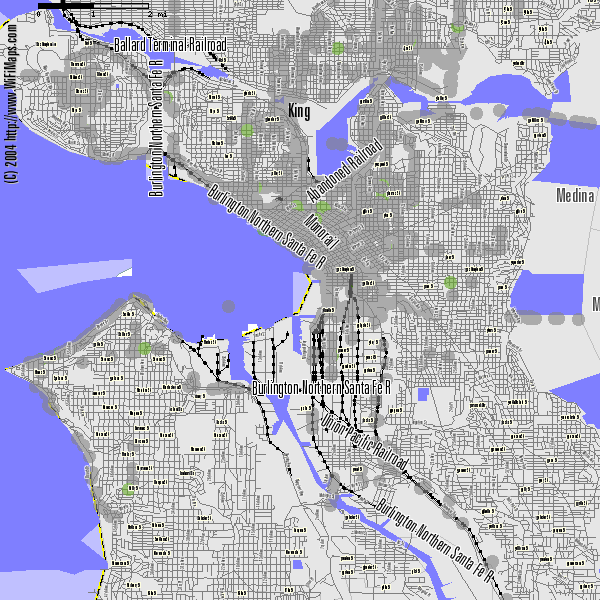
wifimaps.com
Protecting your network
Basic tools you can use to protect your wireless networks (by increasing protection and complexity):
- "Closed" networks
- MAC filtering
- WEP encryption
- WPA encryption
- Strong end-to-end encryption
Closed networks
By turning off beacons, you can prevent your network from being shown in network scan utilities.
Advantages: Standard security feature supported by virtually all access points.
Disadvantages: "Closed" networks are not easily found in a site survey, and are easily found by passive monitoring tools.
MAC filtering
A MAC filter may be applied to an access point to control which devices may be permitted to associate.
Advantages: Standard security feature supported by virtually all access points.
Disadvantages: MAC tables are inconvenient to maintain. Also, MAC addresses are transmitted in the clear (even when using WEP encryption), and are easily copied and reused.
Encryption basics
- Encrypting information is easy
- Key distribution is difficult
- Unique identification is a challenge with wireless
- Public key cryptography solves many (but not all) problems
WEP encryption
Part of the 802.11 standard, Wired Equivalent Privacy provides encryption at layer two.
Advantages: Standard security feature supported by virtually all access points.
Disadvantages: Shared key, numerous security flaws, long-term maintenance impossible on large networks.
WEP problems in detail
- Problems are not with RC4, but with the WEP implementation
- Incompatible key lengths: 40-bit vs. 64-bit vs. 104-bit vs. 128-bit ...
- IV reuse (2^24, or 16 million possible IVs)
- Weak IVs
- Shared key management is difficult
- Offline attacks are simple
Advanced 802.11 features
- 802.1x: EAP-MD5, Cisco LEAP, Microsoft EAP-TLS
- Fast WEP re-keying
- WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
WPA
- TKIP + 802.1x == WPA
- 802.1x can provide mutual authentication of client and AP
- EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, LEAP, PEAP
- Administration is moderately difficult, but possible
- AES + 802.1x == 802.11i
- Very good for private networks, nearly useless for public networks
WPA encryption
While WPA (802.11i) will likely become the standard for protected Wi-Fi access, we are not there yet.
Advantages: Significantly stronger protection than WEP, open standard.
Disadvantages: Vendor interoperability problems, complex configuration, protection only on layer two.
Strong encryption software
Good end-to-end security software should provide strong Authentication, Encryption, and Key Management.
Examples include:
- SSH
- SSL
- IPSec
- OpenVPN
- PPTP
Man-in-the-middle
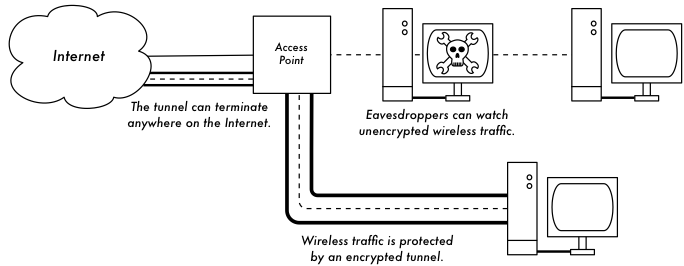
The main problem with implementing encryption at layer two is the possibility of man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
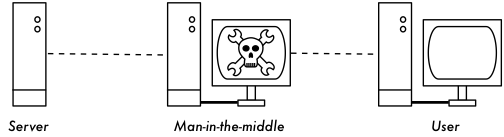
Encrypted tunnels
End-to-end encryption provides protection all the way to the remote end of the connection.
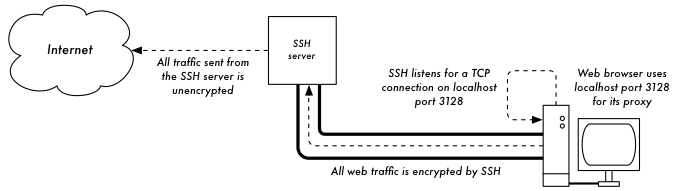
SSH
In addition to providing simple shell access, SSH is a general-purpose tunneling tool.
Security tools
There are hundreds of free tools that will show you lots of information about your network:
- Network ESSID scanners
- Wireless protocol analyzers
- Port scanners / penetration testing tools
- Packet sniffers
- Packet creation tools
- Encryption crackers
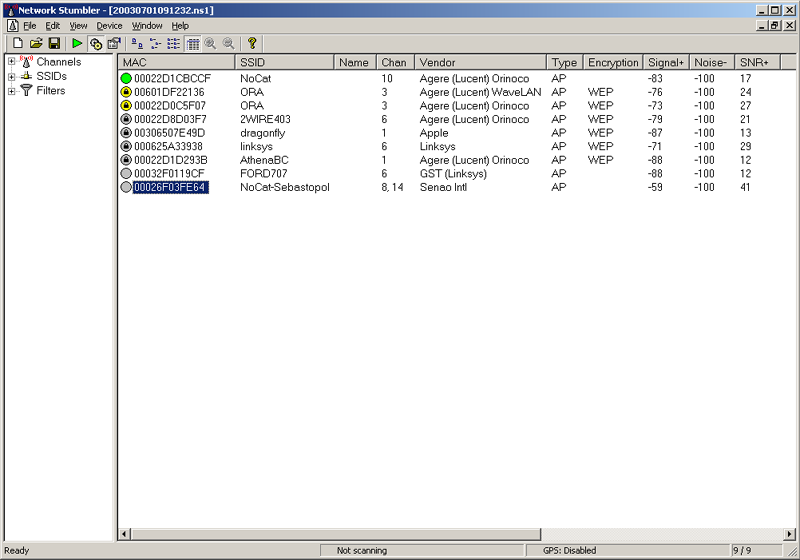
Network ESSID scanners
- Built-in clients
- NetStumbler (Windows)
- MiniStumbler (Pocket PC)
- MacStumbler (Mac OS X)
- Wellenreiter (Linux)
NetStumbler: find networks
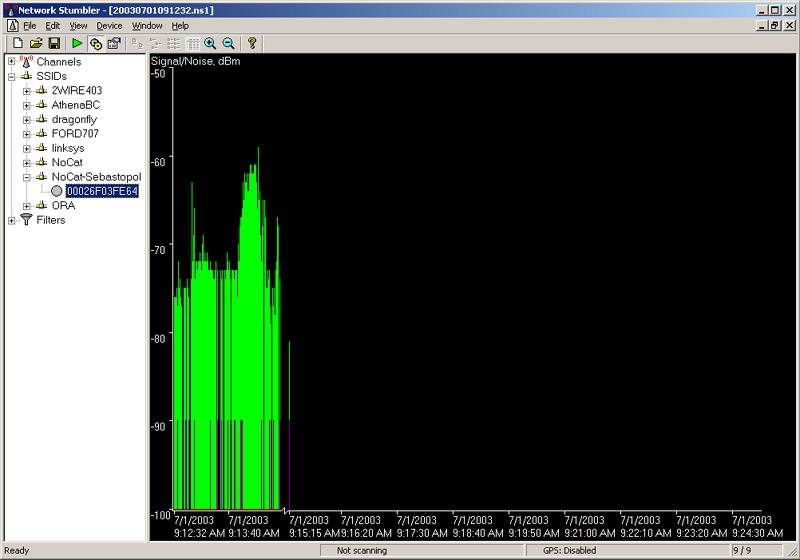
NetStumbler: signal strength
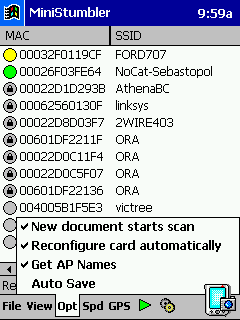
MiniStumbler
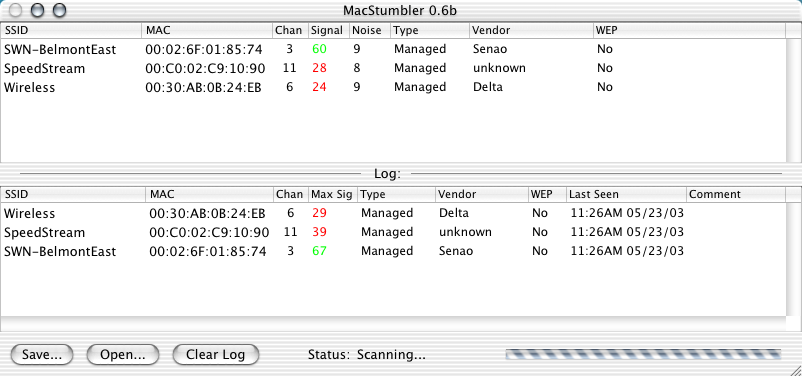
MacStumbler
Wellenreiter

Protocol analyzers
There are a variety of wireless protocol analyzers available. Some include:
- AiroPeek (Windows)
- KisMAC (Mac OS X)
- Kismet + Ethereal (many platforms)
AiroPeek

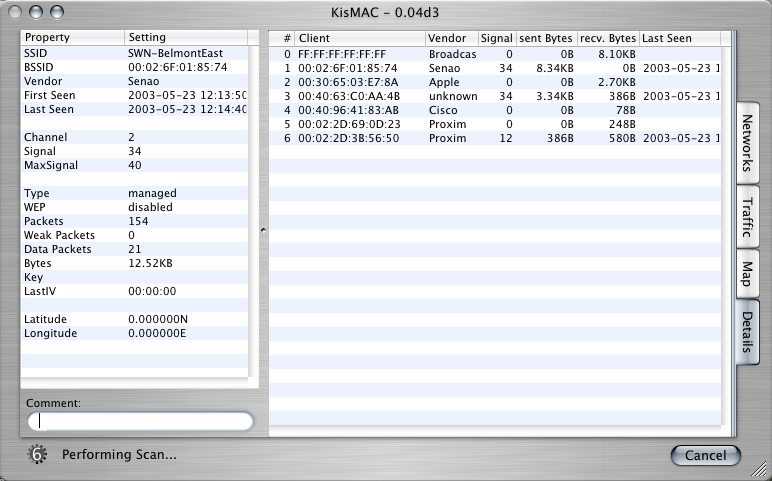
KisMac: details
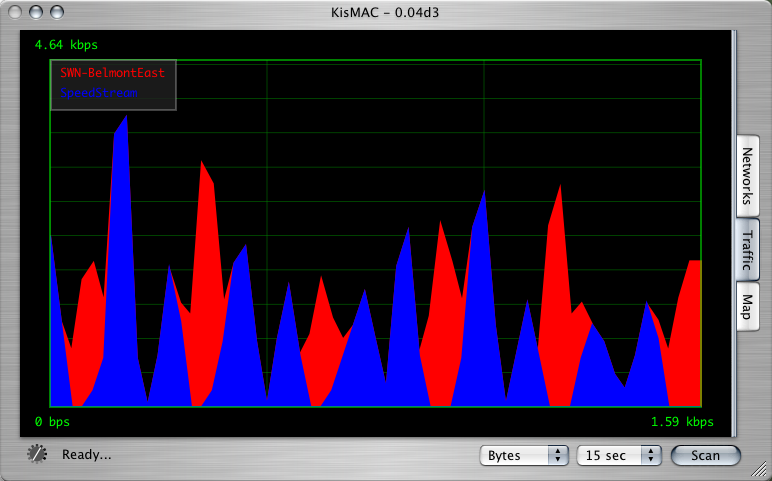
KisMac: traffic
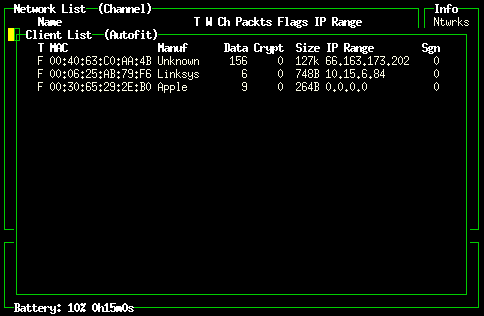
Kismet: networks
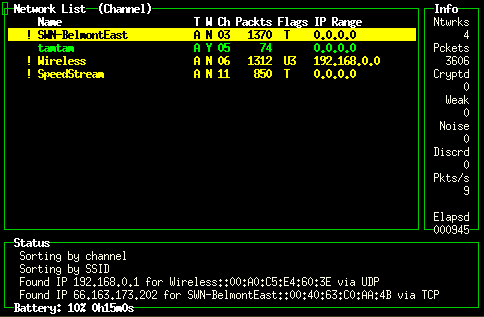
Kismet: info
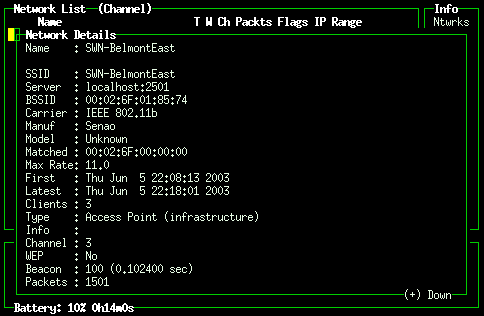
Kismet: clients
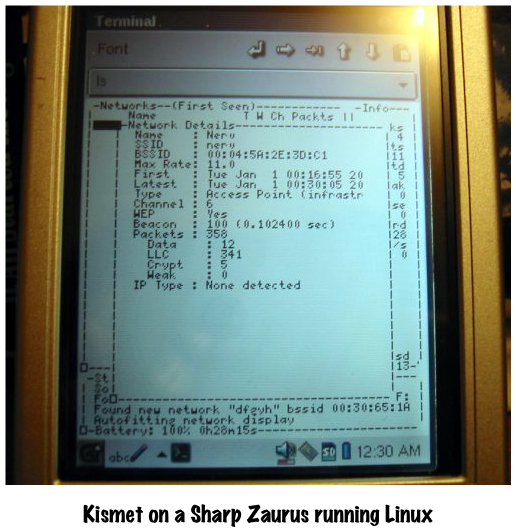
Kismet on a Zaurus
Ethereal and Kismet: beacons
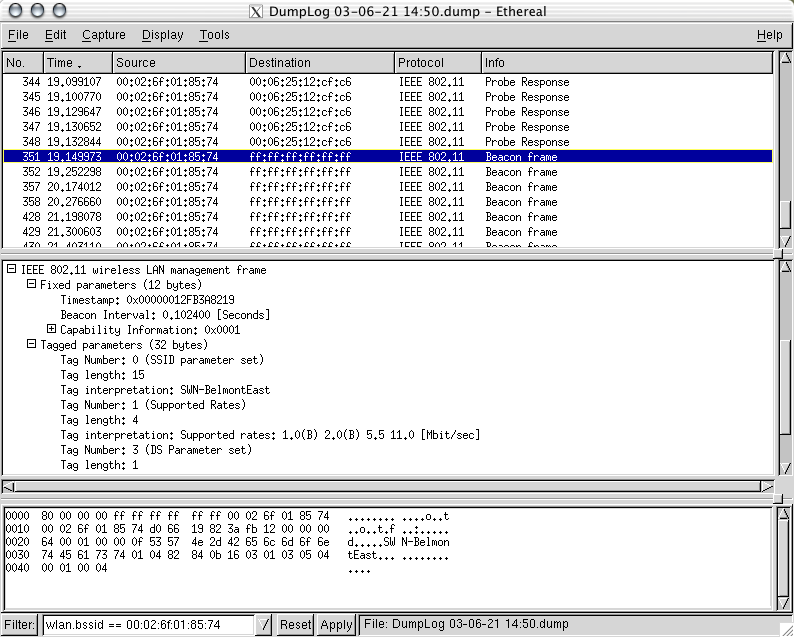
Ethereal and Kismet: filters
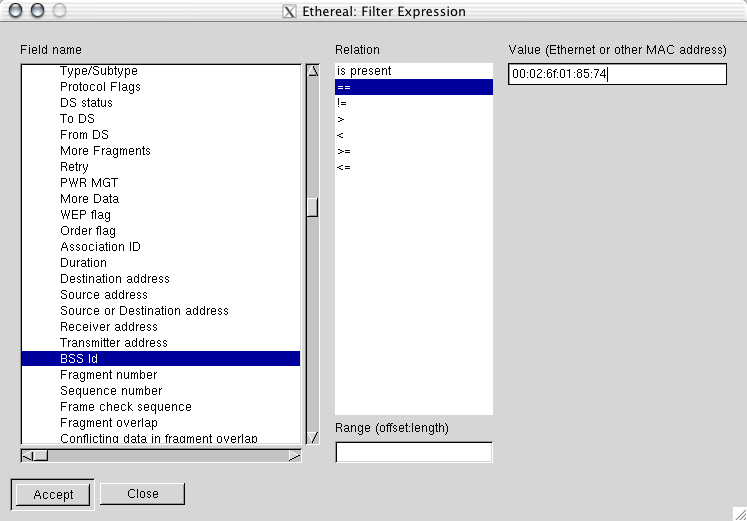
Ethereal and Kismet: WEP
nmap

Ethereal
Ethereal: http decode
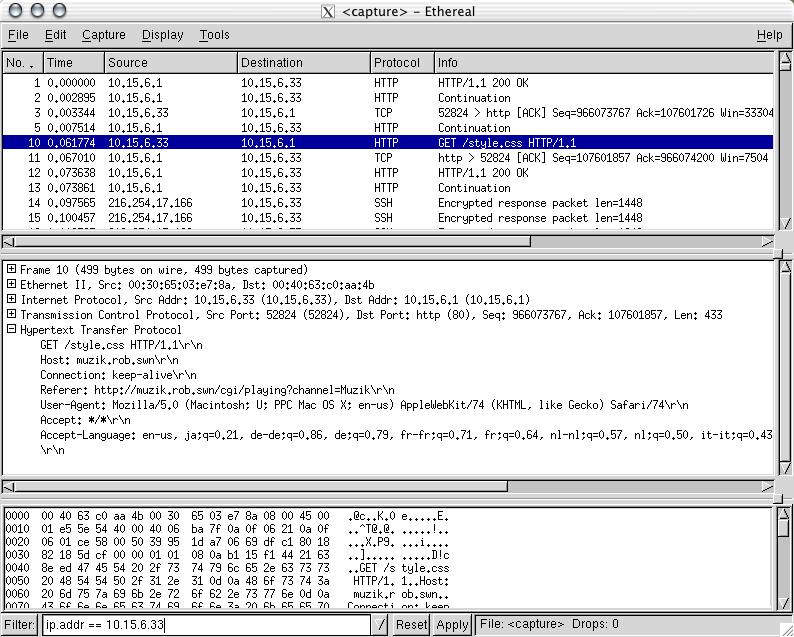
Ethereal: TCP session
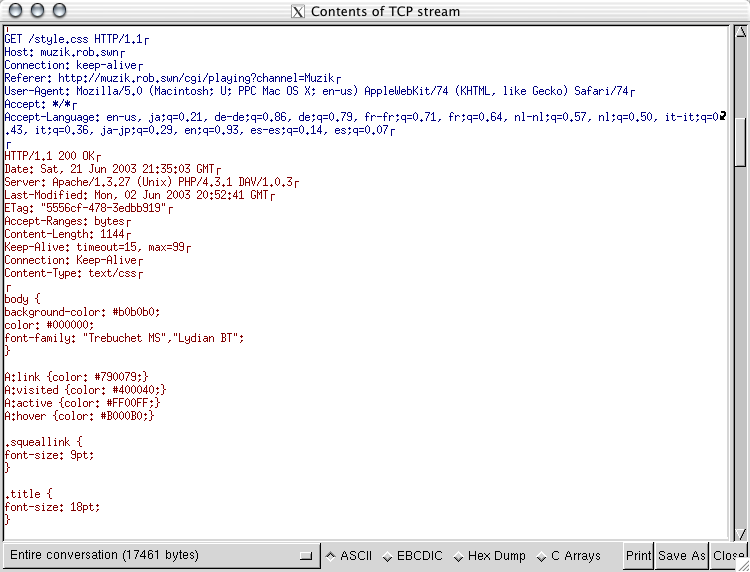
Etherpeg
Driftnet

ngrep

ettercap

airsnort

ntop

ntop: flows
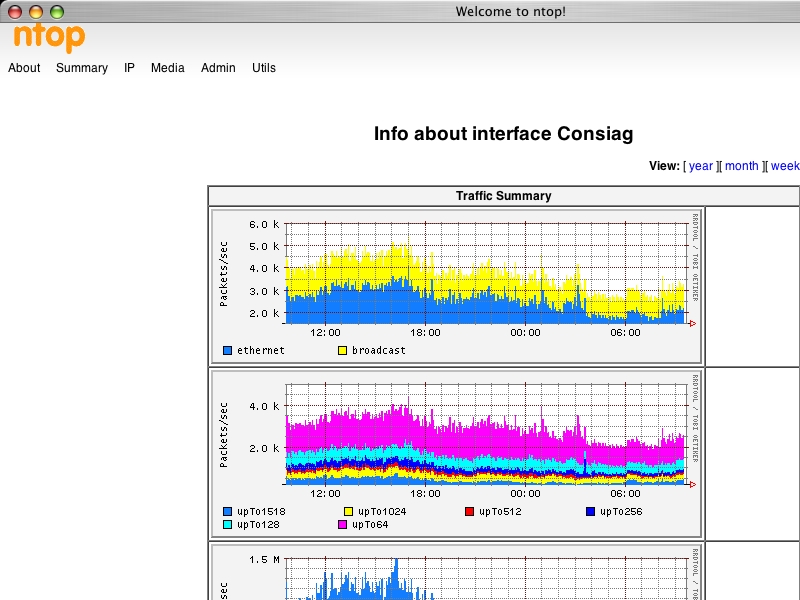
ntop: info
In Summary
Using the proper tools, you can see precisely what is happening on your network.
By using strong end-to-end encryption, you can prevent others from using these tools to attack your networks.
The use of strong end-to-end encryption can also make it safe to use completely untrusted networks (from a public wireless AP all the way to the Internet).
Credits
Portions of this talk were adapted from Wireless Networking in the Developing World, http://wndw.net/
