INETERNET TELEPHONY – BENEFITS, OPTIONS, PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS
OLUMIDE SUNDAY ADEWALE
Department of Industrial Mathematics & Computer Science
Federal University of Technology, Akure, Nigeria
OUTLINE
- What is Internet Telephony?
- Differences between traditional and Internet telephony
- Factors that make Internet telephony possible
- Internet telephony options
- Benefits of Internet telephony
- Technical Barriers
- Solutions to the technical barriers
- Internet telephony future developments
- Conclusion
- 1. What is Internet telephony?
- Internet telephony is the transport of telephone calls over the Internet, no matter whether traditional telephony devices, multimedia personal computers or dedicated terminals part in the calls and no matter whether the calls are entirely or only partially transmitted over the Internet.
- The possibility of voice communication travelling over the Internet, rather than the PSTN, first became a reality early in 1995 when Vocaltec Inc. introduced its Internet Phone software.
- Designed to run on a 486/133 MHz (or higher) personal computer that was equipped with a sound card, speakers, microphone, and modem.
- The software compresses the voice signal and translates it into IP telephony packets.
- Only possible if both parties are using the Internet Phone software.

Personal Computer Configuration for Internet Telephony
- Differences between traditional and Internet telephony
- signal from the Internet telephony must be digital rather than analog for a portion of the transmission.
- Data are packet switched over a shared circuit rather than circuit switched over a dedicated circuit.
- Data follow the TCP/IP protocol of the public Internet.
- Factors responsible for the possibility of Internet telephony
- increase in voice quality
- improvement in compression techniques
- full-duplex personal computer sound cards, enable two-way simultaneous calls
- more powerful personal computers emerging every moment, making it possible to perform processor-intensive functions without specialised hardware
- Internet telephony technology options
- Until the end of 1996, Internet telephony required in most cases a computer, equipped with microphone and speakers, special software for the telephony service at the both sides, a network connection and a subscription to Internet via an ISP. With such requirements, Internet telephony could only be used by a limited number of people.
- There have been three options in the Internet telephony:
- PC-to-PC
- Phone-to-Phone
- PC-to-Phone or Phone-to-PC
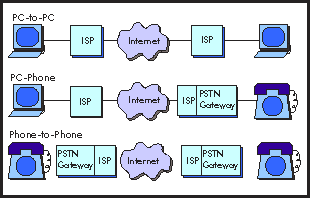
Internet Telephony Technologies (Source: Jupiter Comms.)
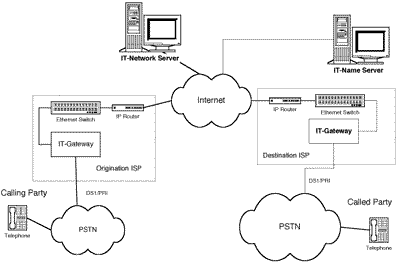
- Benefits
- The most significant benefit of Internet telephony and driver of its evolution is money saving and easy implementation
- Customers take advantage of flat Internet rating versus hierarchical rating and save some money while letting their long-distance call to be routed via Internet
- Deployment of new Internet telephony services requires significantly lower investment in terms of time and money than in the traditional PSTN environment
- Its software oriented nature will make it to be easily extended and integrated with other services and applications
- Internet telephony with an intranet enables users to save on long-distance bills between sites; they can make a point-to-point phone calls via gateway servers attached to the local area network.
- Technical Barriers
The ultimate objective of Internet telephony is, of course, reliable, high-quality voice service, the kind that users expect from the PSTN.
- inter-operability between Internet telephony products and services
- issues to be addressed are:
- codec format
- the transport protocol
- directory services
- Voice performance is measured by delay
- Calls on the PSTN usually exhibit delay of 50 – 70 ms
- This latency increases substantially on the Internet ranges from 500 ms
- Human can tolerate about 250 ms
- Internet is an open network of many different ISP’s networks
- There is no way to get network bandwidth and latency guaranteed
- Loss of packet affects the quality of voice
- Traffic collision and congestion
- Packets take different routes to destination
- Phone-to-phone option using Internet telephony only possible where ISP has POP in the local area
- More digits to dial to get through (ISP, user account, user’s password, and destination phone number)
- Solutions
- ITU H.323 specification ratified in May 1996
- Defines how voice, data and video traffics will be transported over IP-based LANs
- It incorporates the T.120 data conferencing standard
- Recommendation is based on RTP/RTCP for managing audio and video signals
- Part of the recommendation is G.729 for audio codec
- RTP, a new layer to provide support for applications with real-time properties
- RTP to rely on RSVP
- RTP provides a time-stamp and control mechanisms for synchronising different streams with time properties
- LDAP likely to be standard for Internet telephony director services
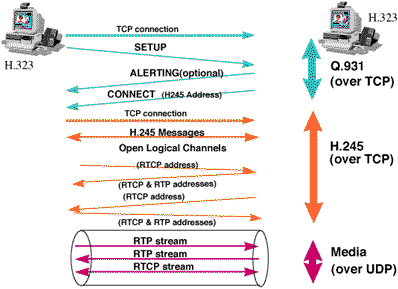
H.323 Call sequence
Quality
- A dedicated service lines with managed traffic loads
- Co-locating telephone access with backbone architectures
- Implement ATM as backbone
- Internet telephony future developments
- Corporate intranets and commercial extranets
- More and cheaper internet telephony gateways
- Integration of voice and video services
- Videoconferencing
- Etc
- Conclusion
Internet telephony is a powerful and economical communication option that integrates both telephone networks and data networks together. The ability to use IP networks to carry traditional telephone traffic brings both challenges and opportunities to all the long-distance telephone service companies. Although a lot of difficulties exist, from the technological point of view to social issues, it is believed that it will bring a great change to communication field and bring a new huge market.




